Logic Design for Array-Based Circuits
by Donnamaie E. White
Copyright © 1996, 2001, 2002, 2008, 2016 Donnamaie E. White, WhitePubs Enterprises, Inc.
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Overview
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- Chapter 2 Structured Design Methodology
- Chapter 3 Sizing the Design
- Chapter 3 Appendix = Case Study in Sizing a Design
- Chapter 4 Design Optimization
- Chapter 5 Timing Analysis for Arrays
- Chapter 6 External Set-up and Hold Times
- Case Study: Preventing Hold Violations Due To Clock Skew
- Computing Hold Time in the Register Example
- Minimum Library (Q5000 Series)
- Military Library (Q5000 Series)
- Exercises
- Chapter 7 Power Considerations
- Case Study: DC Power Computation
- Case Study: AC Power Computation
- Chapter 8 Simulation
- Case Study: Simulation
- Chapter 9 Faults and Fault Detection
- Chapter 10 Design Submission
- ASIC Glossary
External Set-Up and Hold Times
Last Edit July 22, 2001
Example - AMCC Q20000 Bipolar Series
At the other end of the complexity spectrum is the AMCC Q20000 bipolar array series. The Q20000 Series specifies its timing using a min/max range and specifies intrinsic set-up and hold times as worst-case.
External Set-up Time (MIL5, COM5)
Given the MAX and MIN libraries, the external set-up time equations for The AMCC Q20000 Series become those shown in Table 6-3. MIL5MAX, MIL5MIN, COM5MAX and COM5MIN equations are shown. Note that for the MIL5MAX equation, the data path uses the MIL5MAXmax data and the clock path uses MIL5MAXmin data.
Table 6-3 Set-Up Time Equations *
| MILITARY: |
|---|
| tsuMIL5MAX = tDMIL5MAXmax
- tCMIL5MAXmin + TsuMIL5MAX
tsuMIL5MIN = tDMIL5MINmax - tCMIL5MAXmin + TsuMIL5MAX |
| COMMERCIAL: |
|---|
|
tsuCOM5MAX= tDCOM5MAXmax - tCCOM5MAXmin + TsuCOM5MAX tsuCOM5MIN = tDCOM5MINmax - tCCOM5MINmin + TsuCOM5MAX |
The equation does not use MIL5MAXmax for the data path and MIL5MAXminfor the clock path. Those two data sets are from two different operating condition extremes. The combination of two extremes of temperature, voltage and process variation can not occur on a single array.
External Hold Time (MIL5, COM5)
Given the MAX and MIN libraries as described before, the external hold time equation becomes those shown in Table 6-4. MIL5MAX, MIL5MIN, COM5MAX and COM5MIN equations are shown. The same rules apply to these equations in terms of what timing data is used to compute the individual delay paths.
Table 6-4 Hold Time Equations
| MILITARY: |
|---|
|
thMIL5MAX = tCMIL5MAXmax - tDMIL5MAXmin + ThMIL5MAX thMIL5MIN = tCMIL5MAXmax - tDMIL5MAXmin + ThMIL5MAX |
| COMMERCIAL: |
|---|
|
thCOM5MAX = tCCOM5MAXmax - tDCOM5MAXmin + ThCOM5MAX thCOM5MIN = tCCOM5MINmax - tDCOM5MINmin + ThCOM5MAX |
* Both MIL5MAX and MIL5MIN or both COM5MAX and COM5MIN set-up and hold times must be computed and the largest external set-up time and the largest external hold time noted on design submission.
The definitions of the terms used in the equations in Table 6-3 and Table 6-4 are given in Table 6-5.
Table 6-5 Terminology Definitions
Defining a "memory macro" as a latch, a flip/flop or an MSI containing one or the other, the terms used in the equations for the MIL5MAX and COM5MAX libraries are defined below. Terms for the other libraries (MIL5MIN and COM5MIN) would be similarly defined.
|
tDMIL5MAXmax data path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro data input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the maximum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the MIL5MAX library. tDCOM5MAXmax data path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro data input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the maximum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the COM5MAX library. tDMIL5MAX min data path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro data input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the minimum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the MIL5MAX library. tDCOM5MAX min data path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro data input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the minimum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the COM5MAX library. tCMIL5MAX max clock path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro clock input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the maximum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the MIL5MAX library. tCCOM5MAX max clock path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro clock input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the maximum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the COM5MAX library. tCMIL5MAX min clock path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro clock input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the minimum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the MIL5MAX library. tCCOM5MAX min clock path propagation delay from the circuit input and up to the memory macro clock input pin; computed using Front-Annotation methodology before layout, Back-Annotation after layout; computed with the minimum values of the Tpd delays and the k-Factors from the COM5MAX library. Tsumacro = Tsu as specified in Section 6 Thmacro = Th as specified in Section 6 |
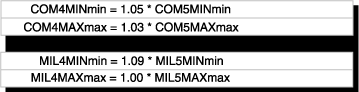
Converting COM5 to COM4, MIL5 to MIL4
The use of adjustment factors, to convert the COM5 and MIL5 data to COM4 and MIL4, were described in Chapter 5. They would also be applied to the computations for external set-up and hold times.
Sample Adjustment Factors (Historical)
![]()
.
Copyright © 1996, 2001, 2002, 2008, 2016 Donnamaie E. White , WhitePubs
Enterprises, Inc.
For problems or questions on these pages, contact [email protected]